What is diabetes?
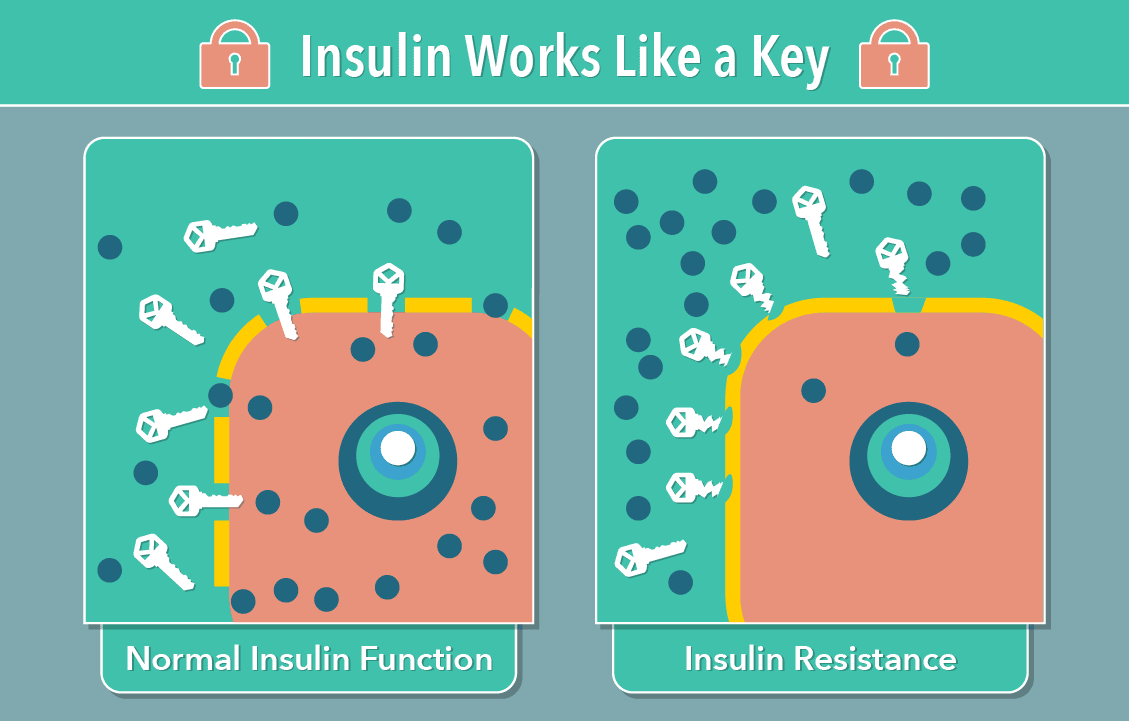
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by high levels of blood sugar (glucose). It occurs due to the body's inability to produce or effectively use insulin, a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels. Think of it like a lock-and-key problem in your body. In a normal body, the cells have doors that can be opened with the key insulin.
This allows the blood sugar to go inside the cells and be used as energy. When you have diabetes, it's as if the locks on your cells are rusty, don't work properly, or there’s no key available. This leads to the glucose staying in your blood causing the increase in blood sugar.
According to a report by the World Health Organization (WHO), there were 422 million adults living with diabetes in 2014, and this number is expected to rise to 629 million by 2045.
In this article, we will explore the types of diabetes, its complications, and effective management strategies.
Types of Diabetes
There are several types of diabetes, each with different causes and risk factors. The most common types include:
- Type 1 Diabetes. Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with T1D need to take insulin injections or use a pump to regulate blood glucose levels. T1D usually develops in childhood or early adulthood.
- Type 2 Diabetes. Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is the most common form of diabetes and accounts for over 90% of all cases. T2D occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin and cannot use it effectively. This results in a build-up of glucose in the blood. T2D is often preventable and can be treated with lifestyle changes, including healthy eating, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Gestational Diabetes. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after the baby is born. Women who develop gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Complications of Diabetes
When blood glucose levels are elevated for prolonged periods, it can result in damage to several organs and systems in the body. The long-term complications of diabetes include:
- Cardiovascular Disease: People with diabetes have an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, such as heart attacks and strokes. High blood glucose levels damage blood vessels, leading to the buildup of plaque, which can block blood flow.
- Kidney Disease: Diabetes is the most common cause of kidney disease. Over time, high blood glucose levels damage blood vessels in the kidney, leading to kidney failure.
- Eye Disease: Diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels of the eye, leading to vision problems, including blindness.
- Nerve Damage: High blood glucose levels can damage nerves in the body, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain, primarily in the hands and feet.
Managing Diabetes
Effective management of diabetes requires a collaborative effort between the individual living with diabetes and their healthcare team. The following strategies are used to manage diabetes:
- Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels: Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential in managing diabetes. Blood glucose levels can be monitored using a glucose meter. The readings provide information to help adjust insulin doses or other medications.
- Healthy Eating: A balanced diet that is high in fiber and low in processed sugar can help manage blood glucose levels.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve blood glucose control and reduce the risk of complications.
- Insulin and Medications: People with diabetes may need insulin injections or other medications to regulate blood glucose levels.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups are essential in managing diabetes. Check-ups include blood pressure, cholesterol, kidney function, and eye exams.
Ready to Join MyCGMCoach?
Covered by Medicare, Medicaid, Aetna, CareFirst, Humana, UnitedHealthcare, and more.


Kunal Sood, MD
Medical Director
